Ashoka Mody, Visiting Professor of International Economic Policy at Princeton University
Beginning in the mid-1980s, the prevailing belief among Indian and international observers was that the authoritarian Chinese regime would mismanage its economy, while democratic India would emerge as the bigger and more developed of the two. Instead, India is now paying the price for underinvesting in its human capital.
In March 1985, the Wall Street Journal showered India’s new prime minister, Rajiv Gandhi, with its highest praise. In an editorial titled “Rajiv Reagan,” the newspaper compared the 40-year-old Gandhi to “another famous tax cutter we know,” and declared that deregulation and tax cuts had triggered a “minor revolution” in India.
Three months later, on the eve of Gandhi’s visit to the United States, Columbia University economist Jagdish Bhagwati was even more effusive. “Far more than China today, India is an economic miracle waiting to happen,” he wrote in the New York Times. “And if the miracle is accomplished, the central figure will be the young prime minister.” Bhagwati also praised the reduced tax rates and regulatory easing under Gandhi.
The early 1980s marked a pivotal historical moment, as China and India – the world’s most populous countries, with virtually identical per capita incomes – began liberalizing and opening up their economies. Both countries elicited projections of “revolution” and “miracle.” But while China grew rapidly on a strong foundation of human-capital development, India shortchanged this aspect of its growth. China became an economic superpower; projections of India as next are little more than hype. The differences have been long in the making. In 1981, the World Bank contrasted China’s “outstandingly high” life expectancy of 64 years to India’s 51 years. Chinese citizens, it noted, were better fed than their Indian counterparts. Moreover, China provided nearly universal health care and its citizens – including women – enjoyed higher rates of primary education. The World Bank report highlighted China’s remarkable strides toward gender equality during the Mao Zedong era. As Nicholas Kristof and Sheryl WuDunn note in their 2009 book Half the Sky, China (particularly its urban areas) became “one of the best places to grow up female.” Increased access to education and the higher female labor-force participation rate resulted in lower birth rates and improved child-rearing practices. Recognizing China’s progress in developing human capital and empowering women, the Bank made an unusually bold prediction: China would achieve a “tremendous increase” in living standards “within a generation or so.” Rather than tax cuts or economic liberalization, the World Bank report focused on a historical fact recently emphasized by Brown University economist Oded Galor. Since the dawn of the Industrial Revolution, every instance of economic progress – the crux of which is sustained productivity growth – has been associated with investments in human capital and higher female workforce participation.
To be sure, market liberalization greatly helped Chinese and Indian growth. But China built its successful development strategy on the twin pillars of human capital and gender equality, areas where India has lagged far behind.
Even after it became more market-oriented, China invested impressively in its people, outpacing India in raising education and health standards to levels necessary for an internationally competitive workforce. The World Bank’s 2020 Human Capital Index – which measures countries’ education and health outcomes on a scale of 0 to 1 – gave India a score of 0.49, below Nepal and Kenya, both poorer countries. China scored 0.65, similar to the much richer (in per capita terms) Chile and Slovakia.
While China’s female labor-force participation rate has decreased to roughly 62% from around 80% in 1990, India’s has fallen over the same period from 32% to around 25%. Especially in urban areas, violence against women has deterred Indian women from entering the workforce.
Together, superior human capital and greater gender equality have
enabled much higher Chinese total factor productivity growth, the most
comprehensive measure of resource-use efficiency. Assuming that the two
economies were equally productive in 1953 (roughly when they embarked on
their modernization efforts), China became over 50% more productive by
the late 1980s. Today, China’s productivity is nearly double that of
India. While 45% of Indian workers
are still in the highly unproductive agriculture sector, China has
graduated even from simple, labor-intensive manufacturing to emerge, for
example, as a dominant force in global car markets, especially in electric vehicles.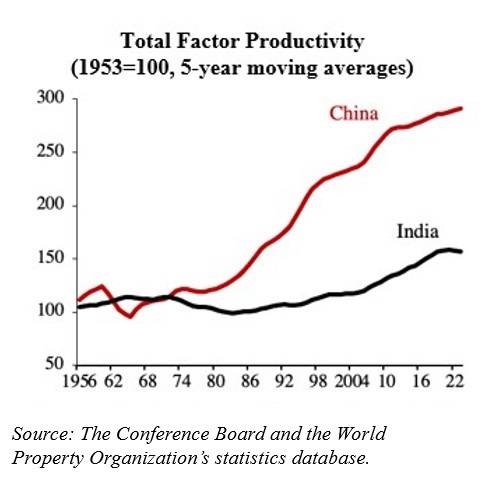
China is also better prepared for future opportunities. Seven Chinese universities are ranked among the world’s top 100, with Tsinghua and Peking among the top 20. Tsinghua is considered the world’s leading university for computer science, while Peking is ranked ninth. Likewise, nine Chinese universities are among the top 50 globally
in mathematics. By contrast, no Indian university, including the
celebrated Indian Institutes of Technology, is ranked among the world’s
top 100.
Chinese scientists have made significant strides in
boosting the quantity and quality of their research, particularly in
fields such as chemistry, engineering, and materials science, and could soon take the lead in artificial intelligence. As the figure shows, Chinese researchers, both in academia and industry, are rapidly generating high-quality patents. 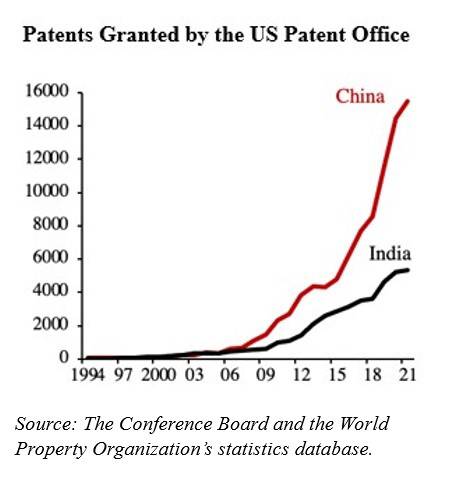
Since the mid-1980s, Indian and international observers have predicted that the authoritarian Chinese hare would eventually falter, and the democratic Indian tortoise would win the race. Recent events – China’s harsh zero-COVID restrictions, rising youth unemployment, and the adverse repercussions of the Chinese authorities’ ham-handed efforts to rein in the country’s overgrown real-estate sector and large tech companies – seem to support this view.
But while China, with its deep well of human capital and greater gender
equality, stands poised at the frontiers of both the old and the new
economies, Indian leaders and their international counterparts tout an ahistorical ability to leapfrog
over a fragile human foundation with shiny digital and physical
infrastructure. China has a plausible path through its current muddle.
India, by contrast, risks falling into blind alleys of unfounded
optimism.
No comments:
Post a Comment
Comments are moderated and generally will be posted if they are on-topic.